Heat pumps are heavily favored by federal incentives and state regulations nowadays, but they may not be right for everyone.
Especially if you live in California, you have two compelling reasons to choose a heat pump over a furnace when it comes time to upgrade your home’s heating system.
There are two types of rebates: the HEEHRA and the utility rebates. It provides rebates of up to $8,000 for the installation of a new heat pump system as part of the Inflation Reduction Act (IRA), which Congress passed in 2022. Secondly, the California Air Resources Board recently voted to ban the sale of new gas furnaces by 2030. It is possible that other states will follow.
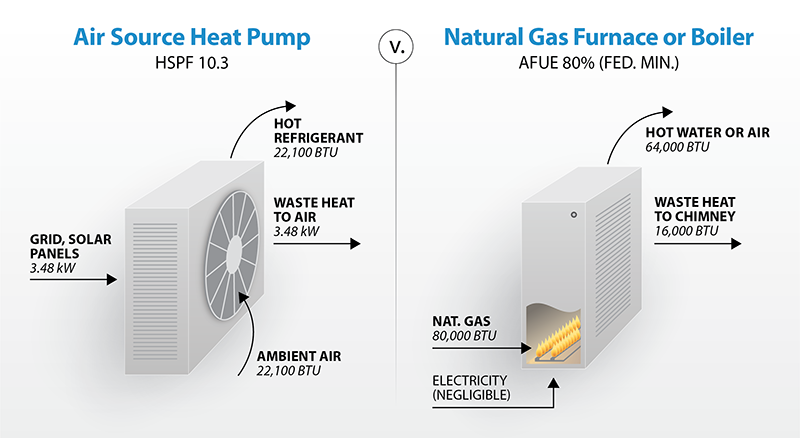
How did heat pumps become so popular? Their main advantage is that they run on electricity and do not emit harmful emissions. Heat pumps are significantly more energy-efficient than electric furnaces, of course.
Even when the outside temperature drops to minus-10 degrees, heat pumps will keep a home comfortable.
What Is a Heat Pump?
Heat pumps work like reverse air conditioners.
The warm air that normally dissipates outdoors would blow into your house if you turned your window air conditioner upside down. With a reversible valve, heat pumps can function as air conditioners and heaters.
As with your refrigerator, heat pumps use a copper coil, refrigerant, and compressor as their cooling system. Heat is released when the compressor compresses the refrigerant and turns it into a liquid.
By vaporizing in the evaporator coils, the pressurized liquid pulls heat out of the air as it sprays through the aperture. A re-pressurization cycle follows. The evaporator coils of an air conditioner circulate cool air into the house, while the coils of a heat pump circulate warm air.
There are two parts to a heat pump. Compressors, evaporative coils, and fans are housed in outdoor units. It is usually separated from the outside unit by an air handler, which houses more condensing coils and a fan. Indoor and outdoor coils are connected by a hose running through the wall.
For individual rooms, mini-splits, which are smaller units with fans, are also available.
What Is a Furnace?
Heat is generated by burning fuel or through the passage of electricity through resistive elements in a furnace unlike a heat pump. A blower inside the air handler circulates heat through the ductwork by circulating it through a ductwork system located in the basement or utility room.
Heat sources, heat exchangers, and blowers are all included in furnaces. Flues exhaust combustion gases from some fuel-burning machines.
Gas furnaces with high efficiency do not require flues. Their PVC drain pipe emits only acidified water and recycles combustion gases for more heat. California plans to ban them even though they convert nearly 100 percent of their fuel into heat.
Consider This When Choosing a Heat Pump vs a Furnace
If you’re building a new house or upgrading your heating system, the HEEHRA incentives make heat pumps a good choice. It is usually the most reliable option to use a furnace in climates below minus-10 degrees.
Combined with resistive heat strips in the air handler, a heat pump might work when your house is airtight and adequately insulated.
Heat Pump Pros and Cons
Pros
-
Low operating costs: When compared with oil or propane furnaces, heat pumps cost half as much to operate as natural gas or electric furnaces.
-
Low installation costs: High-efficiency furnaces cost about half as much to install as conventional furnaces. Installing costs can be seriously impacted by the government incentive. Additionally, heat pumps also cool, so you won’t have to buy air conditioners.
-
Space saving: Heat pumps mount their working parts outdoors and require only 24 inches of clearance. Even less clearance is required for the indoor unit. It is often mounted on the wall along with the air handler.
Cons
-
Not for cold climates: Heat pumps that use air source don’t work well in freezing temperatures. By installing a ground- or water-source system, you can avoid this problem. In that case, pipes would need to be buried underground or underwater, which is an expensive endeavor.
-
Noisy: The compressor produces the most noise, which can be loud enough to disturb nearby residents.
Furnace Pros and Cons
Pros
-
Quiet and unobtrusive: It is possible to hide a furnace in a closet or basement. It may make some noise when the gas is ignited or when air blows through the registers, but apart from that it is very quiet.
-
Less maintenance: Changing filters and vacuuming are all that’s required. Monitoring and maintaining coils and compressors is not necessary.
-
Longer lasting: Furnaces last on average five years longer than heat pumps and are less complicated than heat pumps.
Cons
-
High operating costs: Heat pumps typically have lower operating costs than furnaces.
-
Source of air pollution: Standard-efficiency furnaces with flues emit combustion gases. The cost of buying and installing high-efficiency furnaces is higher, but they don’t pollute.
Making the Final Decision
In general, heat pumps and standard-efficiency furnaces are about the same in terms of cost, so your choice depends largely on where you live.
The decision to go with a heat pump is a no-brainer in moderate climates, especially with government incentives. For extremely cold climates, furnaces are a better choice since they provide more reliable heat.
Ask your neighbors if they use heat pumps and if they are satisfied with them if your climate is between moderate and extreme. Consult your local HVAC dealer as well. The technology of heat pumps is constantly improving, and you might soon find one that meets your needs.